What is CMMI?
Capability Maturity Model Integration is a framework for process improvement and is developed by Software Engineering Institute for Software Development, Service Providers and Organization involved with Acquisitions. Currently, there are three models that address the following:
- The development of Software Products and Services i.e. CMMI–DEV
- The acquisition of Products and Services i.e. CMMI–ACQ
- The establishment, management, and delivery of services i.e. CMMI–SVC
Every CMMI model
- is a process improvement approach that provides organizations with the essential elements of effective processes
- can be used to guide improvement across a team, project, division, or entire organization, and helps to set process improvement goals and
- priorities, provide guidance for quality processes, and provide a point of reference for appraising current processes.
Current models version is 1.3. There are common elements in all these three different models, as shown in the following diagram: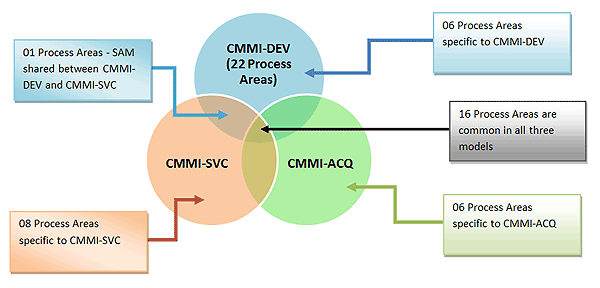
CMMI Processes are divided into following two categorizations:
- Maturity Level wise
- Category wise
Maturity Level wise categorization of CMMI Process Areas:
Organizations not having any Maturity Level are at Maturity Level 1. SEI only provides CMMI Assessment for organizations from Maturity Level 2. Maturity level wise Process Areas are divided into following five categories:
1. Maturity Level 1 – Initial
- NO PROCESS AREA
2. Maturity Level 2 – Managed
- Configuration Management
- Measurement and Analysis
- Project Monitoring and Control
- Project Planning
- Process and Product Quality Assurance
- Requirements Management
- Supplier Agreement Management
3. Maturity Level 3 – Defined
- Decision Analysis and Resolution
- Integrated Project Management
- Organizational Process Definition
- Organizational Training
- Organizational Process Focus
- Product Integration
- Requirements Development
- Risk Management
- Technical Solution
- Validation
- Verification
4. Maturity Level 4 – Quantitatively Managed
- Organizational Process Performance
- Quantitative Project Management
5.Maturity Level 5 – Optimizing
- Causal Analysis and Resolution
- Organizational Performance Management
Category wise categorization of CMMI Process Areas:
Category wise Process Areas are divided into following four categories:
1. Project Management
- Integrated Project Management (IPM)
- Project Monitoring and Control (PMC)
- Project Planning (PP)
- Quantitative Project Management (QPM)
- Requirements Management (REQM)
- Risk Management (RSKM)
- Supplier Agreement Management (SAM)
2. Engineering
- Product Integration (PI)
- Requirements Development (RD)
- Technical Solution (TS)
- Validation (VAL)
- Verification (VER)
3. Process Management
- Organizational Performance Management (OPM)
- Organizational Process Definition (OPD)
- Organizational Process Focus (OPF)
- Organizational Process Performance (OPP)
- Organizational Training (OT)
4. Support
- Causal Analysis and Resolution (CAR)
- Configuration Management (CM)
- Decision Analysis and Resolution (DAR)
- Measurement and Analysis (MA)
- Process and Product Quality Assurance (PPQA)
Process Areas and their use in CMMI
There are 22 process areas in CMMI and each process area represents an activity needs to be followed to achieve a Maturity Level. This section describes Process Areas and their purpose.
1. Project Planning (PP)
Project Planning process area provides best practices like estimation, project plan preparation including resource planning, scheduling, risk plan etc. and taking commitment. Project Planning Process Areas helps implementers in effective project planning.
2. Project Monitoring and Control (PMC)
Project Monitoring and Control (PMC) process area provides guidance for project management techniques for monitoring through progress reviews, meetings, milestone reviews, status reporting etc. and controlling of issues.
3. Configuration Management (CM)
Configuration Management (CM) process area helps in establishing and maintaining the integrity of work products (artifacts). It provides guidance for identification of Configuration items, control of configuration, status accounting of work products and configuration audits.
4. Integrated Project Management (IPM)
Integrated Project Management (IPM) process area helps in establishing and managing the project and the involvement of relevant stakeholders. It guides for tailoring of standard process for development of project defined process.
5. Measurement and Analysis (MA)
Measurement and Analysis (MA) process area guides for development and sustaining measurement capability within projects leading to management of measurement at org level. It helps in decision making by senior management.
6. Process and Product Quality Assurance (PPQA)
Process and Product Quality Assurance (PPQA) process area helps in managing the quality of processes and products by using audits and quality assurance activities.
7. Decision Analysis and Resolution (DAR)
Decision Analysis and Resolution (DAR) process area help in selecting the best alternative using formal evaluation technique.
8. Quantitative Project Management (QPM)
Quantitative Project Management (QPM) process area is advance measurement and help in quantitative control and improvement of the projects objectives derived from business goals.
9. Risk Management (RSKM)
Risk Management (RSKM) process area helps in identification of potential problems before they occur and planning their mitigation activities planning and taking action on their occurrence.
10. Supplier Agreement Management (SAM)
Supplier Agreement Management (SAM) process area help in the management of the products and services acquired from suppliers.
11. Requirements Management (REQM)
Requirements Management (REQM) process area helps in management of user requirements. It also ensures alignment between the project work and requirements.
12. Requirements Development (RD)
Requirements Development (RD) process area helps in collecting requirements, analyzing them and then detailing them into different requirements like user, customers, product, and product component requirements.
13. Product Integration (PI)
Product Integration (PI) process area helps in assembling the product components into final product and ensuring that the product after integration behaves as intended and deliver the product.
14. Technical Solution (TS)
Technical Solution (TS) process area helps in selecting, designing, and implementing solutions to the project requirements.
15. Validation (VAL)
Validation (VAL) process area helps in ensuring that the product work in its indented environment.
16. Verification (VER)
Verification (VER) process area helps in ensuring that selected work products meet their specified requirements by verifying them.
17. Causal Analysis and Resolution (CAR)
Causal Analysis and Resolution (CAR) process area help in identification of root causes of the issues/defects and then to plan corrective and preventive actions to improve process performance.
18. Organizational Process Definition (OPD)
Organizational Process Definition (OPD) process area helps in establishing and maintaining a library of organizational process assets, work environment standards, and rules and guidelines for teams.
19. Organizational Training (OT)
Organizational Training (OT) process area is associated with the development of skills and knowledge of project team members so they can perform their roles effectively and efficiently.
20. Organizational Performance Management (OPM)
Organizational Performance Management (OPM) process area is to proactive management of the organization’s performance to meet its business objectives.
21. Organizational Process Focus (OPF)
Organizational Process Focus (OPF) helps in planning, implementing, and deploying organizational process improvements. It is based on thorough understanding of current strengths and weaknesses of the organization’s processes and process assets.
22. Organizational Process Performance (OPP)
Organizational Process Performance (OPP) helps in the process improvement activities. It helps in establishing and maintaining a quantitative understanding of the performance of selected processes towards achieving the organizational goals.
Note
For explanation of common terms, please refer to CMMI Terminology.


